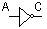
0 1
1 0
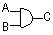
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 1
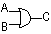
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
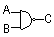
0 0 1
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
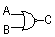
0 0 1
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 0
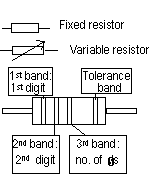
| Black = 0 | Brown = 1 | Red = 2 | Orange = 3 | Yellow = 4 |
| Green = 5 | Blue = 6 | Violet = 7 | Gray = 8 | White = 9 |

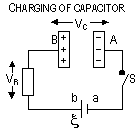
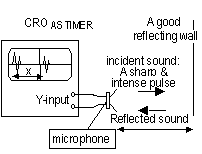
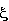 ,
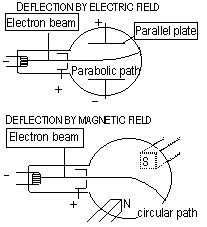
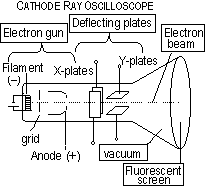
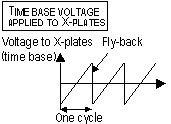
, , (I = VR /R),
e- flow stops;
, (I = VR /R),
e- flow stops; 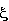 ,
,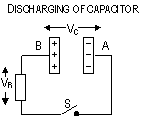
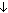 , (charges
, (charges 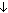 ) > I
) > I 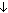 (VR
(VR 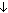 ),
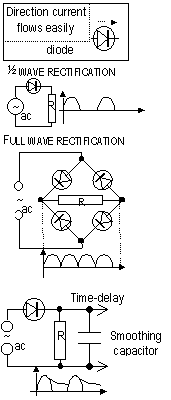
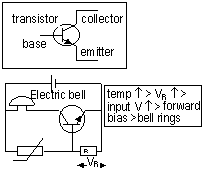
), 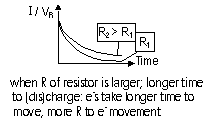
| Gate type | Symbol | Truth table | Statement | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOT | 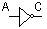
| 0 1 1 0 Output NOT same as input
| AND | 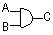
0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 Output high if input A AND B are high
| OR | 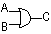
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 Output high if input A OR B OR both are high
| NAND | 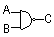
0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 Output NOT high if input A AND B are high
| NOR | 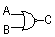
0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 Output NOT high if input A OR B or more inputs are high
| |