Phys4
PRESSURE
Pressure = force acting normally (or perpendicularly) per unit area
Pressure = [Force / Area (p = F / A = N/ m2 = Pa, pascal)] or [density x height x gravity = ρhg (liquid)]
Atmospheric pressure-pressure exerted by air around us, 105 Pa at surface of the earth, decreases with altitude
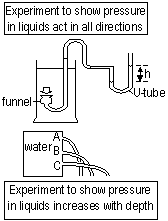
Pressure in liquid-acts in all directions and increases w/ depth
A simple mercury barometer; instrument for measuring atmospheric pressure, consists of inverted thick-walled glass tube filled w/ mercury placed vertically w/ its open end below surface of mercury in a dish, vertical height of mercury column gives atmospheric pressure in mm Hg (vertical height of tube unchanged if tube is tilted, diameter of tube doesn't affect height)
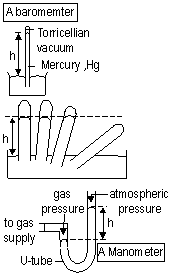
Gas pressure-measured by a U-tube manometer
Pressure of gas = Atmospheric pressure + height = A + h
average value of barometric height at sea-level = 760 mm Hg = standard atmospheric pressure = 1 atmosphere
pressure = density x height x gravity =13600 x 760/1000 x 9.8=101300 N/m2, 760 mm Hg = 101300N/m2 = 1 atmosphere
pressure measured in bars, 1 bar = 105N/m2, 1 millibar = 102N/m2
Isobars; lines on weather maps joining places of equal air pressure
Pressure gradient; diff in pressure across 2 regions, diff v. large, pressure gradient high, wind; high > low pressure
Average pressure at sea level = 1016mb
high pressure = 1030mb: calm, dry weather, morning fog, afternoon sun, low pressure = 990mb: stormy wind, cloud, rain
Temperate latitude-vary rapid pressure changes-cyclones and anticyclones
Light
Magnetism
Electrostatic Charging
Electricity
Thermal Physics
Waves & Sound
Radioactivity
Measurements in Physics
Forces
Energy
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index

