Phys3
ENERGY
chemical-in food, fuels, can be released in chemical reactions
potential-gravitational (energy a body possesses due to it's position or condition) and elastic P.E.-types of mechanical energy
kinetic-type of mechanical energy, energy possessed by all moving bodies
heat-or thermal/internal energy
nuclear-stored in nucleus of atoms, released in fission (nuclei of heavy atoms break up into smaller nuclei) and fusion [(nuclei of lighter atoms fused to together to form larger nuclei) less radioactive waste than fission, less life, uranium]
light (electromagnetic radiation)
sound
magnetic
electrical
(solar- heat + light -focus sun's rays onto small areas with concave mirrors, heat turns water into steam > drive generator turbines, silicon cells can be used for solar heating)
Most energy comes from the sun-
solar-sun's energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions of sun's nuclei (protons combine to helium, large amount of energy released)
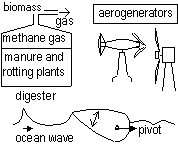
biomass- light energy stored in plants (plants rot methane, for cooking, produced, can be collected if placed in a digestor)
wind-high to low pressure-aerogenerator converts K.E. of wind to electrical energy
waves-caused by wind blowing over the sea
hydro-electric- clean and useful source, stores water which can drive turbines
Moon-tides-caused by moon pulling on the seas
Earth-geothermal-energy (heat) in earth (radioactive decay of elements in core)
Energy-capacity to do work (joules, J), energy needed to do work
amt of work done-shows how much energy has been converted from one form to another
Law of conservation of energy-energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be changed from one form to another
Work-transfer of energy from 1 physical system to another
-done when force produces motion (pt. of application of force moves)
Work = force x dist. moved in direction of force = F d[(Nm=J), 1J = 1N moved through 1m]
Gravitational potential energy = mass x gravity x height = mgh (J)
Kinetic energy = Force x distance = ma x s = ½mv2 (J)
Power (W), rate of doing work = work done (energy transfer)/time = E/t
Efficiency (%) = work output / work input = power output / power input (< 100%, energy lost to overcome friction)
E = mc2, [E = energy, m = decrease in mass, c = speed of light = 3 x 108m/s)
Pressure
Light
Magnetism
Electrostatic Charging
Electricity
Thermal Physics
Waves & Sound
Radioactivity
Measurements in Physics
Forces
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index
