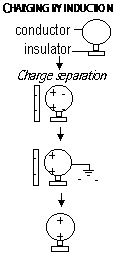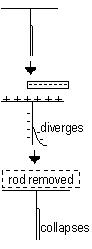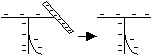Phys7
ELECTROSTATIC CHARGING
Electrostatic charging-charging a material by friction > charged w/ static electricity (causes materials to be attracted to it)
Positive + Negative Charges
Unlike charges attract, like charges repel, gain electrons > -ve charge, lose electrons > +ve charge, + charges = - charges : neutral
Charged material attract uncharged materials: charge on charged material repels like charge on uncharged material away from surface > unlike charge near surface > attracted
Charge
Measured in coulombs (C), 1C=6 x 1018 electrons > 1 electron has a -ve charge of 1.6 x 10-19C
Electrical Insulators and Conductors
Conductors allow charges to move through it; e-s move freely from 1 atom to another (free electrons), metals, carbon, damp skin, water, charged by contact w/ charged bodies & by electrostatic induction
Insulators do not allow charges to flow through them easily: e-s tightly bound to atoms > unable to move freely, sulphur, quartz, paraffin, wax, PVC, silk, charged by friction
Charging by contact- object charged by direct contact w/ charged body, same charge
Charging by induction- conductor is charged by bringing it near a charged body w/o any direct contact, opp charge
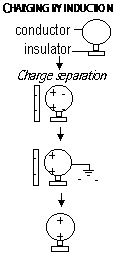
Golden Leaf Electroscope- detects charges and tests sign of charges on a body
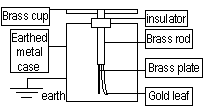
Experiments with a Gold-Leaf Electroscope
To Detect a Charge
-Bring rod near to brass cap > gold-leaf diverges > charge present
-Charge has been induced on the leaf and plate, temporary only
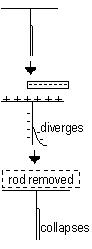
To Charge the Electroscope by Contact
-Touch and roll rod on cap
-Leaf diverges and stays diverged when rod removed
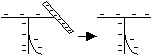
Charging the Electroscope by Induction
-Bring rod near cap
-Earth cap by touching it (e-s flow in /out)
-Remove finger, remove rod
-Leaf stays diverged
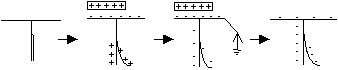
Effect of Charges on a Charged Electroscope
| Charge on Electroscope | Charge brought near cap | Effect on divergence of gold leaf
|
|---|
| + | + | Increases
|
| - | - | Increases
|
| + | - | Decreases
|
| - | + | Decreases
|
| + or - | Uncharged | Decreases
|
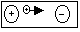
Electric Field- region where electric charges experience electrical forces
Direction at any pt.; given by force on a small +ve charge at that pt., +ve > -ve
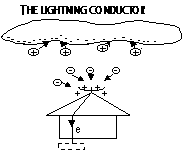
-protects buildings; a thick Cu strip fixed to highest pt. of building and has a sharp-spiked end
-ve charged thunder cloud induces +ve charges on spikes > -ve ions attracted by spikes > e-s are discharged to earth > +ve ions repelled by spikes to clouds > neutralises -ve charged cloud > less likely to produce a lightning flash
Electricity
Thermal Physics
Waves & Sound
Radioactivity
Measurements in Physics
Forces
Energy
Pressure
Light
Magnetism
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index