Phys6
MAGNETISM
Properties of a magnet
-attract only magnetic materials, ferromagnets
-ferromagnets are attracted to poles of magnet which are of equal strength
-a freely supported magnet will always come to rest with the north pole pointing roughly towards the Earth's north pole
-like poles repel, unlike poles attract (force of attraction decreases as separation increases)
Test for a Magnet-Repulsion
Making a Magnet
1. stroking-single or double touch method
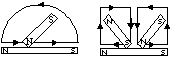
2. electrically
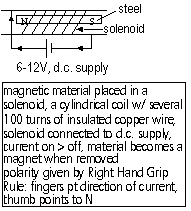
Demagnetizing a Magnet
1. electrically
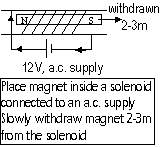
2. heat magnet strongly and let it cool lying in an east-west direction
3. hammer of drop magnet repeatedly
Induced Magnet
Induced magnetism-when a permanent magnet touches a magnetic material, the material becomes a temp. magnet
Magnetic Properties of Iron and Steel
Iron-soft (easily magnetized, and demagnetized), temp + strong magnetism; electromagnets, magnetic shielding
Steel-hard (hard to magnetize and demagnetized), permanent + weak magnetism; permanent magnets
Magnetic Fields
region surrounding a magnet where magnetic forces can be felt, field contains magnetic flux; represented by magnetic lines of force
direction of magnetic flux: N > S, magnetic flux patterns can be traced out by; using iron filings or a compass
Typical Field Patterns
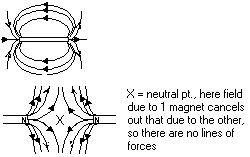
Magnetic Screening/Shielding
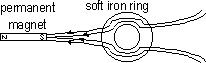
protects delicate instruments affected by external magnetic field, instrument placed in a thick walled soft iron box: soft iron higher magnetic permeability compared to air > magnetic flux is drawn into iron and concentrated through it
Permanent Magnets
Permanent magnets don't lose magnetism readily. There are 2 types - alloy magnets + ceramic magnets
Alloy magnets-contain metals (Fe, Ni, Cu, Co, Al), used in electric generators, motors, loudspeaker + telephones
Ceramic magnets-made from powders called ferrites (iron oxide and barium oxide); coat tapes for tape recorders, computer memory
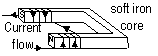
Electromagnets; temp magnets: soft iron core magnetised only when current flows in surrounding coil
strength - if-current in coil increases, if # of turns in the coil increases, if the poles are closer together
Used in electrical devices, electric bell, relay, switch
Electrostatic Charging
Electricity
Thermal Physics
Waves & Sound
Radioactivity
Measurements in Physics
Forces
Energy
Pressure
Light
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index





