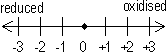Chem6
CHEMICAL REACTIONS + ELECTROLYSIS
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Oxidation-gain of oxygen
-loss of hydrogen
-loss of electrons
-gain in oxidation number
Reduction-loss of oxygen
-gain of hydrogen
-gain of electrons
-reduction in oxidation number
Oxidation Numbers
-elements = 0
-simple ions (non-radicals) = charge
-hydrogen = +1 , joined directly to metals(hydride ion = -1)
-oxygen = -2 , peroxides = -1
-compounds and radical have sum of oxidation numbers = total charge
Oxidation numbers used for :
-identifying oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions (redox reaction-when there is a change in oxidation #s; electrons transferred)
-identifying what has been oxidised and reduced
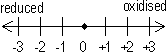
Oxidizing agent(reduced) takes e-
Reducing agent (oxidised) gives e-
KI: tests for oxidizing agents [KI; colourless > brown]
K2Cr2O7 + KMnO4: test for reducing agents [K2Cr2O7; orange > green, KMnO4; purple > colourless]
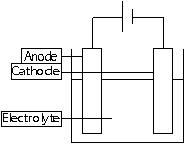
ELECTROLYSIS
Electrolysis = process where electrical energy is used to make a chemical reaction occur at the electrodes (current passed through electrolyte)
Electrodes = made of solid conductors Cathode =-tive electrode, cations are attracted to it Anode =+tive electrode, anions are attracted to it
Electrolyte = Solution or molten liquid that contains ions, where current is passed through
easily oxided > K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Sn > H > Cu > Ag > Au > easily reduced
low conc.: SO42- + NO3- > Cl- > Br- > I- > OH- > easily oxidised
high conc.: SO42- + NO3- > OH- > Cl- > Br- > I- > easily oxidised
Electrodes; inert / reactive, reactive; Cu , reactive electrodes oxidised before anoins
Electrolysis; uses:
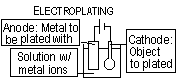
Electroplating; metal to be plated = anode (oxidised), object to be plated = cathode (reduced), electrolyte = solution w/ metal ions to be plated
chromium-bumper bars, shiny parts of cars, tin-cans, silver-jewellery, cutlery
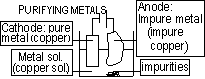
Purifying (Refining) metals; impure metal > anode (oxidised), metal reduced as pure metal at cathode
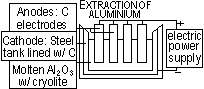
Extraction of Metals from ores; bauxite >Al2O3, Al2O3 m.p. >2000°C, 950°C :cryolite (Na3AlF6) dissolves Al2O3, save energy,$ & reduce pollution
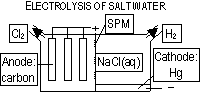
Electrolysis of salt water; conc. salt water electrolysed > H2 + Cl2 + NaOH
Rate and Heat of Reactions + Reversible Reactions
The Periodic Table
Metals
Organic Chemistry
Non-metals
The Particulature Nature of Matter
Experimental Techniques
Atoms, Elements and Compounds
Stoichiometry + Mole Concept
Acids, Bases and Salts
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index