Chem11
NON-METALS
Hydrogen
Reactions producing hydrogen
Reactive metals + water:
reactive metals (K - Mg) react w/ water to produce H2
Metals + acids:
metals (^H) + dilutes acids
Electrolysis of aqueous sol:
electrolysis of solutions- if cation in sol is ^H
Methane + steam:
CH4 + H2O > CO + 3H2
Uses of hydrogen:
make NH3, margarine (unsaturated veg oil + H2 >(Ni)> margarine), fuel for rockets
Uses of water:
Industry- soft drinks, chemicals, drugs
Home- drinking, cooking, washing
Purification of water
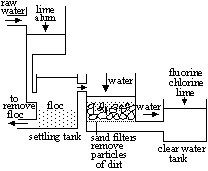
Sedimentation- suspended solids settle out of water > sediment deposited by gravity
Flocculation- lime & alum added to raw water > tiny suspended particles stick together > larger particles/clumps = flocs (v.fine fluffy mass)
Filtration- after flocculation, suspended matter (large, fine) removed from water (using medium permeable to water but not material)
Sterilisation- chlorine added to water to kill (remove) bact
Test
Hydrogen
-pop test: 2H2 + O2 > 2H2O
Water:
-hydration of anhydrous CuSO4 crystals (white/ pale green solid > blue), -cobalt paper: blue > pink
Oxygen
Uses:
Respiration
-combustion of sugars in body cells
glucose + O2 > CO2 + H2O + energy
Combustion
-subs + O2 > energy
Rusting
-slow oxidation of Fe in presence of oxygen & moisture to Fe2O3
(brown solid)
4Fe + 3O2 > (H2O) > 2Fe2O3
Methods of rust prevention
-prevent water & oxygen from reaching Fe or steel: cover w/ paint, oil/ grease, tin, chromium
-galvanise w/ zinc: sacrificial protection, zinc corrodes 1st > oxide layer
-stainless steel: Cr or Ni added to Fe
Test
-make burning splint burn brightly, rekindles a glowing splint
Uses of oxygen
-bottled oxygen assists ppl breathing difficulties, -space shuttles, fuel, -make steel O2 passed over Fe > burns off impurities, -oxy-acetylene torch: acetylene gases (hydrocarbons) & O2 mixed > weld iron & steel
Volume composition of air
N2: 79%, O2: 20%, noble gases (mainly argon) <1%, CO2: 0.03%, water vapour: variable
Air pollution: harmful subs- CO, SO2, oxides of N, Pb compounds and CFC's
Sources of air pollutants
CO: poisonous gas formed in incomplete combustion of fuels, causes headaches, heart damage
SO2: combustion of fuels in fuels in power stations, oil refineries and extraction of metals in industries, causes breathing difficulties > bronchitis & lung cancer, acid rain (SO2 + H2O > H2SO3- sulphurous acid)
NOX: combustion of fuels in motor vehicles and industries, damages lungs, acid rain (NO2 + H2O > - nitrous acid)
Pb compounds: combustion of leaded petrol, causes brain damage, affects heart kidneys
CFC: from aerosol s, coolants in refrigerators, thins ozone layer > allows UV rays to penetrate atmosphere > skin cancer
O2 & N2 obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air
Nitrogen
unreactive gas, important elements in plants & animals, used in amide linkage of proteins
Haber process
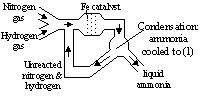
N2 + 3H2 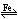 2NH3 + E
2NH3 + E
Pressure: 200 atm (speed up rate of reaction), temp 450°C (too high: reverse reaction favoured, too low: too slow), catalyst: Fe
NH3 removed when reaction 15% complete as at equilibrium under the conditions only 15% of reaction is completed
Ammonia produced: heat ammonium compounds (w/ bases)
N (make proteins), P, K important in quick & healthy plant growth, need to be water soluble to be included in fertilisers (NH3 + acid sol > solid which is crystallised from solution- NH3 + HNO3 > NH4NO3, NH3 + H2SO4 > (NH4)2SO4)
Sulphur
S: gun-powder, S burns > SO2, uses of SO2: bleach (in manufacture of paper), food preservative (kill bact), make H2SO4
Contact Method
-the method of producing H2SO4
make SO2: S + O2 > SO2
make SO3: 2SO2 +O2 <-> 2SO3 + E (2-3 atm, 450C, catalyst: vanadium(V) oxide: V2O5)
dissolve SO3 in H2SO4: SO3 + H2SO4 > H2S2O7
(difficult & dangerous to dissolve directly in water > 96% H2SO4 used)
dilute H2S2O7 to make conc H2SO4: H2S2O7 + H2O > 2 H2SO4
H2SO4: strong acid: reacts w/ bases, metals, carbonates, conc H2SO4 used as dehydrating agent and oxidising agent, H2SO4: used in making fertilisers, detergents, plastics, synthetic fibres, paints, dyes (SO2: reducin

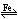 2NH3 + E
2NH3 + E