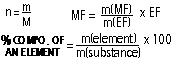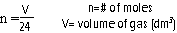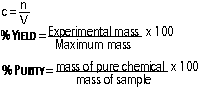Chem4
STOICHIOMETRY+MOLE CONCEPT
Acid: chemicals in H2O that make H+ +anion
Hydrochloric acid = HCl
Nitric acid = HNO3
Acetic (ethanoic) acid = CH3COOH
Sulphuric acid = H2SO4
Phosphoric acid = H3PO4
salt: ionic substances made from metal cation + anion from acid
ACID+METAL > SALT+HYDROGEN
METAL (BI)CARBONATE > (HEAT) > METAL OXIDE/(CARBONATE)+CARBON DIOXIDE
ACID+(BI)CARBONATE > SALT+WATER+CARBON DIOXIDE
ACID+BASE > SALT+WATER [Neutralisation]
METAL+OXYGEN > METAL OXIDE
METAL OXIDE+WATER > METAL HYDROXIDE (BASE)
NON-METAL+OXYGEN > NON-METAL OXIDE
NON-METAL OXIDE+WATER > NON-METAL HYDROXIDE (ACID)
Relative masses
Relative Atomic Mass = average mass of the atom compared with 1/12 of the mass of carbon-12
Ar=(avg.mass of 1 atom of the element) (1/12 of mass of one atom of C) [nucleon/mass number of an element]
Relative Molecular mass (Mr) = mass of 1 mole of compound (sum of relative atomic masses of atoms)
(Relative Formula Masses-ionic + macromolecular compounds)
Avagadro's Number = 6.02 x 1023 (one mole)
One mole contains 6.02 x 1023 particles
Atomic Weight = weight of 1 mole of atoms of that element, in grams (nucleon number)
Molecular Weight = weight of 1 mole of that substance, in grams (sum of atomic weights of atoms)
Empirical Formula=simplified whole number ratio of moles of compound
Molecular Formula = complete formula
[n = number of moles, m = mass (g), M = molar mass (molecular weight)]
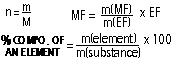
Spectator ions = ions in a reacting solution, do not react themselves (cancelled out)
Solubility
Solid ionic compounds exist in the form of ionic lattices
When ionic compounds dissolve ions in the lattice dissociate (break away from one another) and become ions in the water
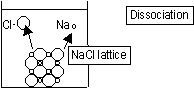
Some compounds have forces that can't be broken by water, dissociate a little-insoluble
Solubility rules
Acetates + Nitrates + Bicarbonates = all soluble
Sulphates = all soluble, except Ba+ and Pb2+ (Ca+ slightly soluble)
Chlorides + Bromides + Iodides = all soluble, except Ag+ and Pb2+
Carbonates + Phosphates = all insoluble, except K+, Na+ and NH4+, Li+
Hydroxides + Oxides = all insoluble, except K+, Na+ and Ba+ (Ca+ slightly soluble)(NH4+ = soluble)
Li+, Na+, K+, NH4+ salts are all soluble
Law of Conservation of Mass: Mass of Reactants = Mass of Products
In chemical reactions mass is conserved, not lost or gained
Molar Volumes = amount of space taken up by one mole of a chemical (solids + liquids-small, but different)
Gases-large and equal molar volumes at r.t.p. (room, temperature and pressure)
ALL GASES = 24 dm3
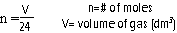
Concentration of Solutions: amount of solute (usually solid) in 1dm3 of solution
[c = conc. (mol/dm3), n = # of moles, v = volume (dm3), 1000cm3 = 1 dm3]
Limiting Reactants:-reactants 1 in excess, other limiting. limiting reactant/reagent used up, the reaction stops
Acids + Bases
Chemical Reactions + Electrolysis
Rate and Heat of Reactions + Reversible Reactions
The Periodic Table
Metals
Organic Chemistry
Non-metals
The Particulature Natrue of Matter
Experimental Techniques
Atoms, Elements and Compounds
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index