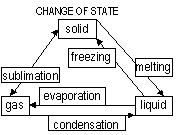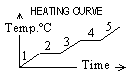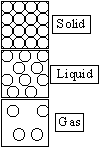
| Property | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attraction force | Strong | Weak | None |
| Movement | Slow (vibrate about a fixed pos.) | Faster than solid (w/o a fixed pos.) | Very fast (random) |
| Arrangement of particles | Regular (close, no spaces) | Random (close, small spaces) | Random (far apart, big spaces) |
| Hardness | Hard | Soft | None |
| Density | High | Moderate | Very low |
| Compressibility | None | None | Yes |
| Diffusion | Little/none | Slow | Fast |
| Shape | Definite | Indefinite | Indefinite |
| Volume | Definite | Definite | Indefinite |