Chem2
EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES
Indicators
-chemicals (usually extracted from plants) that change colour at different pH
pH-measure of acidityacid pH>7, neutral pH=7, alkaline pH<7
methyl orange [red > orange(pH4) > yellow]screened methyl orange [red > grey (pH4) > green]
litmus [red > - (pH7) > blue]phenolphthalein [colourless > - (pH9) > pink]
Criteria of Purity
to prove a substance is pure/impure-melting point (pure-1 m.pt., impure: >1 m.pts.)
-boiling point (pure-1 b.pt., impure-distils over >1 b.pts.)
-chromatogram (pure-1 spot)
Measuring Melting Point
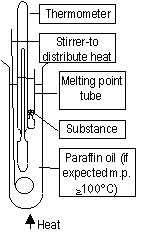
Heat, substance begins to melt > temp. remains constant = melting point, impure: melts over a range ot m.p.'s
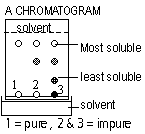
Paper Chromatogram (colour-graph)
Chromatography-used to identify mixtures and testing for purity. separate colourless substances: locating agent colours colourless spots. Spots identified by RF value = dist. moved by substance/ dist. move by solvent
Spots separate due to different solubility in solvent
More soluble, moves faster + farther
Chromatography used to separate and identify complicated substances e.g. dyes in food, drugs in urine, pesticides in vegetables, proteins and sugar
Methods of Purification
Mixtures separated into pure substances by purification-a method/methods to make a substance pure(separating mixtures into pure substances)
1.filtering-separates solids from liquids-suspended solids are removed
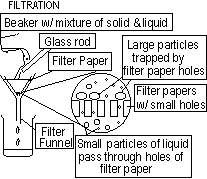
2.dissolving-separates solid(solute) from solid mixtures by using a solvent
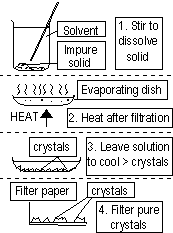
3.crystallising(evaporation)-separates solid(solute, dissolved) from solution
4.Sublimation-separates solid from solid mixture by changing 1 to gas
5.Distillation-separates solvent in solution
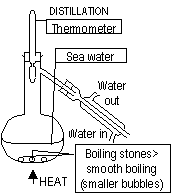
6.Fractional distillation-separates 2/> miscible liquids-
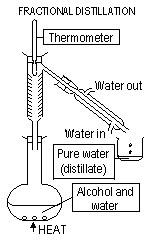
7.Chromatography-separates solid or liquid mixtures-separates and purifies mixture
Industry-petrol, etc separated from crude oil, spirits form fermented liquor, gases in liquid air
Purity important in food and pharmaceutical industry, impurities;-reduce effectiveness of drug, etc, cause side effects, make drug dangerous
Atoms, Elements and Compounds
Stoichiometry + Mole Concept
Acids + Bases
Chemical Reactions + Electrolysis
Rate and Heat of Reactions + Reversible Reactions
The Periodic Table
Metals
Organic Chemistry
Non-metals
The Particulature Natrue of Matter
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index





