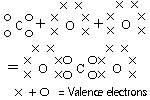Chem3
ATOMS, ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS
ATOM-made of sub-atomic particles, electrons, protons, neutrons

| | Relative mass | Relative charge | Symbol
|
| proton | 1 | +1 | p+
|
| electron | 0 (1/1840) | -1 | e-
|
| neutron | 1 | 0 | n0
|
# of electrons = # of protons in an atomnucleus = protons + nucleons
proton(atomic)number-#of protons in an atomnucleon(mass)number-# of protons and neutrons in nucleus of an atom
isotopes-atoms with same proton number but different nucleon number
isomers-same atoms different structural config.
Isotopes
-non-radioactive
radioactive-give out harmful radiation which is harmful to life
-produces energy (235U in nuclear reactors)
-kill germs and cancer cells (60Co-sterilize surgical instruments)
Electron Arrangement
All chemical reactions, chemical properties and most physical properties are due to electrons
Electrons arranged in shell around nucleus in an atom
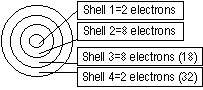
Last/outer shell = valence shell (valence electrons=group #)
full valence shell = stable =noble gases
Atoms > gain/loses/share e- > stable e- config. (gain/lose e-s-make bonds-a strong force of attraction between +& -)
Ionic Substances
Ion =atom w/ a +/- charge (lose/gain electron) ion neutral
all metals-lose electrons (+ ion)non-metal-(many) gain electrons (-ion)
noble gases-remain single atoms, very stable
atoms form chemical bonds with each other to get stable electron config.
e-H →[H]+ or
H → H+, (e- = valence electron),
Hydrogen ion: H+
|
Acetate: |
CH3COO-
|
|
Aluminium: |
Al3+
|
|
Ammonium: |
NH4+
|
|
Barium: |
Ba2+
|
|
Bicarbonate: |
HCO3-
|
|
Bisulphate: |
HSO4-
|
|
Bromide: |
Br-
|
|
Calcium: |
Ca2+
|
|
Carbonate: |
CO32-
|
|
Chloride: |
Cl-
|
|
Copper II: |
Cu2+
|
|
Fluoride: |
F-
|
|
Hydrogen: |
H+
|
|
Hydroxide: |
OH-
|
|
Iodide: |
I-
|
|
Iron III (ferric): |
Fe3+
|
|
Lead: |
Pb2+
|
|
Lithium: |
Li+
|
|
Magnesium: |
Mg2+
|
|
Nitrate: |
NO3-
|
|
Oxide: |
O2-
|
|
Phosphate: |
PO43-
|
|
Potassium: |
K+
|
|
Silver: |
Ag+
|
|
Sodium: |
Na+
|
|
Sulphate: |
SO42-
|
|
Sulphide: |
S2-
|
|
Zinc: |
Zn2+
|
|
Dichromate: |
Cr2O72-
|
|
Nitride: |
N3-
|
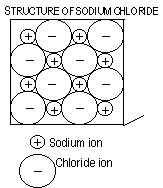
Ionic Bonding (Metal+Non-metal)
Lattice-a giant structure of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction between the ions (continuous bonding)
In the reaction (electron transfer) between metal and non-metal electrons are lost and gained
Properties
Not volatile(high m.pt+b.pt.)-many strong bonds (a lot of energy to break)
Hard-many strong bonds
Brittle-ions of similar charge forced together > repel > break lattice
Soluble in water ;usually
Non-conductor of electricity as solids-charged particles are not mobile to carry electricity
Conductors of electricity as liquids + (aq) -has mobile charged particles to carry electricity
Magnesium oxide (MgO)-lining inside of furnaces- very high m.pt. + heat resistant-refractory
Covalent Molecules (Non-Metal+Non-Metal)
Substances compete for electrons, share electrons-covalent bond
A molecule-a group of atoms bonded to each other, have no bonds to other atoms, just weak forces of attraction
Covalent molecules: strong bonds in molecule, weak forces of attraction between molecules
Covalent bond represented by "-"
single bond-2 electrons shareddouble bond-4 electrons sharedtriple bond-6 electrons shared
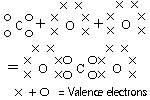
Properties
Volatile(low m.pt.+b.pt.)- weak forces attraction between molecules
Soft-weak forces of attraction between molecules
Non-conductors of electricity*-no charged particles
*except if they react with water > form solutions containing ions [CO2,HCl(gas),NH3]
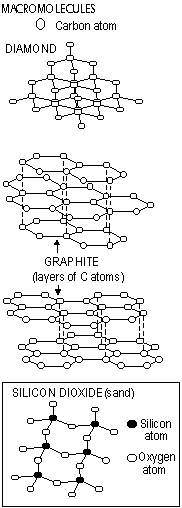
Macromolecules (Covalent networks) (non-metal+non-metal)
Exist as atoms joined by covalent bonds to other atoms. Bonding continuous for large number of atoms
Macromolecules-diamond, graphite, silicon dioxide, polymers
Properties
Low volatility- many strong bonds
Hard*-many strong bonds
Non-conductors of electricity**-no mobile/charged particles
*except graphite-soft: weak forces of attraction between layers
*except graphite-conductor: mobile delocalised electrons(not used for bonding, free and mobile to carry electricity)
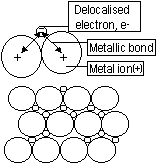
Metals
They are metal ions that have delocalised ions. Ions attracted to delocalised ions-metallic bond
Properties
Low volatility*-many strong bonds
Hard-many strong bonds
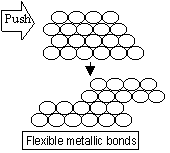
Malleable(will go flat when hit)/ductile(ability to be made into wires)-flexible metallic bonds (electrons move + form new bond)
Conductors of electricity-mobile charged particles (delocalised electrons)
*Mercury-volatile-weaker metallic bonds (Group I metals-volatile)
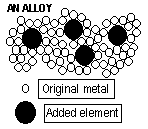
Alloys
Mixture of a metal with another element, which changes the metal's properties (usually to make it more stable)
Steel-Fe + C-vehicles, ball bearings, medical instruments, tools, utensils
Brass-Cu + Zn-pins of electric plug, water pipes(plumbing)
Stoichiometry + Mole Concept
Acids + Bases
Chemical Reactions + Electrolysis
Rate and Heat of Reactions + Reversible Reactions
The Periodic Table
Metals
Organic Chemistry
Non-metals
The Particulature Natrue of Matter
Experimental Techniques
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index