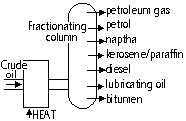
| Fraction | # of C atoms | BP range (°C) | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum gas | 1 - 4 | < room temp | gas for gas cookers |
| Petrol | 5 - 10 | 35 - 75 | petrol: cars |
| Naptha | 8 - 12 | 70 - 170 | petrochemicals |
| Kerosene/ paraffin | 10 - 14 | 170 - 250 | fuel: aircraft, kerosene-lamps |
| Diesel | 15 - 25 | 250 - 340 | fuel: buses, lorries |
| Lubricating oil | 19 - 35 | 340 - 500 | lubricant, waxes & polishes |
| bitumen | > 70 | > 500 | black substance to surface road mixed w/ chemical > tar |
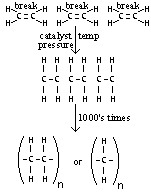
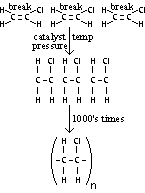
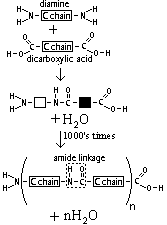
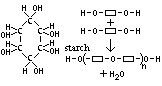
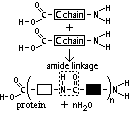
 )
) 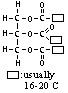
| Natural polymer | Monomer | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Starch | Glucose | Provide energy (energy store in plants) |
| Protein | Amino acid | For growth, enzymes |
| Fats | Long-chained carboxylic acid + glycerol | Provide energy |
| Cellulose | Glucose | Energy store |
| Synthetic polymer | Monomer | Uses |
|---|---|---|
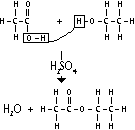
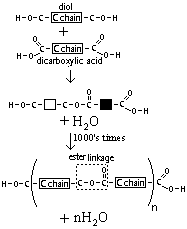
| Terylene (polyester) | Diol + dicarboxylic acid | To make fibres for clothing |
| PVC- polyvinylchloride | Chloroethene | Water pipes, waterproof plastic sheeting, insulation for cables & wires |
| Polyethene | Ethene | Make plastic (film- wrapping, bottles, pipes,...) |
| Nylon | Diamine + dicarboxylic acid | strong fibres () |