Bio2
ENZYMES
Enzymes-Biological organic catalysts, speed up chemical reactions w/o being consumed in the process. Reappear at end of process. They are proteins affected by temperature and pH range, not like inorganic catalysts.
Substrate-substance being acted on by enzymes.
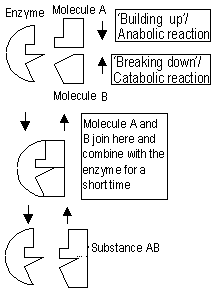
enzyme + substrate ↔ product 1 + product 2 + enzyme
Characteristics of enzymes
Specificity:- due to molecular structure, only certain substrate able to fit properly ('lock and key' mechanism)
Sensitivity to temperature:-low temp.-inactive. Every 10°C rise in temp. -activity doubles
optimum temp.=37°- 40°C, Beyond optimum temp. -activity reduced [enzymes are denatured('killed')]
Sensitivity to pH range:- -most enzymes work best at a specific pH
proteins digesting enzymes=pH 2.5, most intestinal enzymes=pH7.8/8.2.
(pH=hydrogen ion concentration in a solution (measure of acidity or alkalinity). )
-Denaturazation occurs at high acidity or alkalinity.
Enzyme-substrate concentration:-At a given enzyme concentration, increase in substrate will initially increase the rate of enzyme reaction, but if continues to increase the reaction will cease and vice versa.

ROLE OF ENZYMES IN SEED GERMINATION
-Seeds store food materials in cotyledon or endosperm (substitute for cotyledon).
-Store carbohydrates, fats and proteins. During germination water enters seed through micropyle and
activates enzymes. The reserved food materials are digested into simple substances.
-Energy is required to support seed until it produces it's own food.
Carbohydrates > (diatase) > maltaose > (maltase) > glucose
Protiens > (pepsin) > peptone > (erepsin) > amino acids
Fats and oil > (lipase) > fatty acids and glycerol
USES OF DIGESTED FOOD SUBSTANCES
Simple molecules from digestion oxidised > energy released as ATP molecules for germination
Amino acids > new protoplasm, proteins + other organelles
Glucose > new cell wall + other organelles
Fatty acids + glycerol + proteins > plasma membrane of new cells
-Intercellular- enzymes made & have their react inside the cell
E.g.-photosynthesis enzymes inside chloroplasts, respiratory enzymes inside mitochondrion
-Extracellular- enzymes made inside the cell but react outside the cell
E.g.-digestive systems in human gut, enzymes released by saprotrophic fungi and bacteria
Nutrition
Transport in Plants
Support, Movement and Locomotion
Transport system in man-circulatory system
Respiration
Excretion
Homeostasis
The Eye
Nervous System
Chemical Control of Plant Growth
The Use and Abuse of Drugs
Diversity of Organisms
Nutrient cycles and Ecology
Parasitism
The Human Impact on the Environment
Reproduction in plants
Sexual reproduction in animals
Genetics
Cell Structure and Organisation
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index

