Bio15
NUTRIENT CYCLES
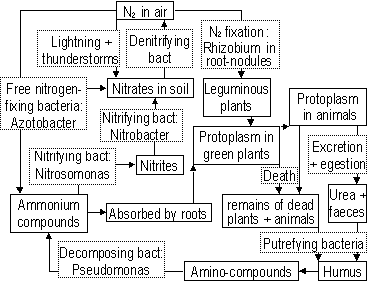
Nitrogen cycle
-atmosphere: 78-79% nitrogen
-N2:
-synthesis of amino acids > proteins > enzymes, hormone, protoplasm
-essential for growth
-synthesis of nucleic acids and chlorophyll
Nitrogen fixation; nitrogen in air > nitrates by organisms (bact.+ blue-green algae), active (requires energy form of ATP molecules), (non-)symbiotic, 1symbiotic: nodules in roots (leguminous), shelter + food for bact., bact, Rhizobium converts nitrogen > nitrates, 2non-symbiotic: bact., Azotobacter in soil: nitrogen > nitrates in soil > absorbed by plants
Ionising events in atmosphere (lightning + thunderstorms)- fixes small amounts N2, nitrogen oxide > HNO3 > nitrates
Decomposition/Putrefaction; decomposers, bact. + fungi, act on dead bodies of plants and animals + excretory & waste products to form humus > amino compounds > ammonium compounds (toxic)
Nitrification; ammonium compounds > nitrites, Nitrosomonas > nitrates, Nitrobacter, nitrifying bact: active, aerobic
Denitrification; nitrates in soil > nitrogen in air, denitrifying bact, anaerboic (soils water-logged), results in reduction of soil fertility (avoid > plough land > improve drainage and aeration > O2)
ECOLOGY
Ecology-study of relationship of living organisms w/ each other & surroundings/ interaction bet. (a)biotic components
biotic environment-all living things, which an organism comes into contact with
habitat-place where an organism lives
ecological niche-organisms function in its habitat
populations-group of individuals (same species) occupying a given area (depends on birth, death/mortality rate & migration)
ecological community-when populations of plants an animals live together under the same environmental conditions
ecosystem-ecological system formed by the interaction of living organism and their non-living environment
ecosystem of living organisms: producers, consumers/ decomposers
producers-green plants that manufacture complex organic food from raw material (CO2, H2O)[only organisms that convert radiant energy into chemical energy that they store]
consumers-feed on other orgnms to obtain energy, primary con.-herbivores, feed directly on plants, secondary con.-carnivore-feed on herbivores, tertiary con.-feed on primary & secondary consumers + producers
predator-animal that feeds on another animal
decomposers-act on dead organisms to get food, materials in dead organisms return to environment to be utilised
Food chain-theoretical relationship bet. producers & consumers, series of orgnsms through which energy flows through
Food web-inter-linking food chains
No energy cycle, energy flow-unidirectional
energy progressively decreasing down food chain, prod.>pri. con. 90% lost, no cellulase: cellulose in producers undigested, pri. con. > sec. con. & sec. Con. > ter. con ; less energy lost, most eaten is flesh, easily digested
Energy lost at every trophic level as heat, respiration , excretory and waste substances, energy used by organism, maintain metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, reproduction, etc
Ecological pyramids
-diagrammatic rep. to show relationships between organisms in an ecosystem
-producers on bottom, then consumers
-each column proportional to numbers
pyramid of numbers: organism of a given area are first counted and grouped into trophic levels > arranged according to trophic levels, carnivores highest trophic level, producer lowest trophic level
pyramid of biomass: total mass, biomass, estimated for each trophic level > weigh organism, dry mass (not wet mass)
pyramid of energy: ideal pyramid to show relationship between organisms, each bar- amount of energy per unit area that flows through the trophic level
Parasitism
The Human Impact on the Environment
Reproduction in plants
Sexual reproduction in animals
Genetics
Cell Structure and Organisation
Enzymes
Nutrition
Transport in Plants
Support, Movement and Locomotion
Transport system in man-circulatory system
Respiration
Excretion
Homeostasis
The Eye
Nervous System
Chemical Control of Plant Growth
The Use and Abuse of Drugs
Diversity of Organisms
Back to 'O' level notes index
Back to notes index
