 -particles
-particles 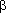 -particles
-particles 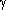 -radiation
-radiation
| Properties |  -particles -particles | 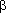 -particles -particles | 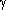 -radiation -radiation |
|---|---|---|---|
| nature | positive particle: helium nucleus, a stream of He nuclei (~7000 times mass of an electron) | stream of high energy e-s, formed from nucleus decay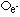 | electromagnetic waves, v.short wavelength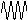 |
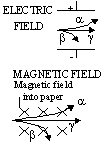
| affected by electric and magnetic fields | Yes | yes, bent strongly | no |
| penetration | stopped by paper or skin or 6cm of air | stopped by 3mm of Al | reduced but no stopped by lead (50%) |
| causes ionisation | Strongly | weakly | very weakly |
| dangerous | yes | yes | yes |
| speed | 10% speed of light | 50% speed of light | speed of light |
| detection | Photographic film, cloud chamber, G-M tube, spark counter, gold-leaf electroscope | photographic film, cloud chamber, G-M tube | photographic film, cloud chamber, G-M tube |
 particles fired at v.thin sheet of gold foil (µm thin), particles detected by zinc sulphide screen mounted on a rotatable microscope (done in dark: can see v.small flash of light when
particles fired at v.thin sheet of gold foil (µm thin), particles detected by zinc sulphide screen mounted on a rotatable microscope (done in dark: can see v.small flash of light when  -particle strikes zinc sulphide screen)
-particle strikes zinc sulphide screen)| Observations | Conclusion |
|---|---|
most  particles passed straight through the foil particles passed straight through the foil | Atoms are mostly made of space |
| some particles were deflected slightly through small angles | Atoms have a +ve charge nucleus |
| v.few particles were scattered backwards | The nucleus is v.small & heavy |
| proton | neutron | electron | |
|---|---|---|---|
| charge | +1 | 0 | -1 |
| mass | 1 unit | 1 unit | 1/2000 units (0) |
| symbol | 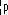 | 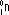 | 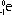 |
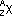
 -particle emitted by nucleus, mass # decreases by 4, atomic # decreases by 2
-particle emitted by nucleus, mass # decreases by 4, atomic # decreases by 2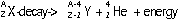
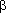 -particle emitted by nucleus, mass # remains the same, atomic # increases by 1
-particle emitted by nucleus, mass # remains the same, atomic # increases by 1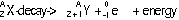
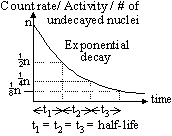
 -particle emitted by nucleus, mass & atomic # remains the same (energy content of nucleus only decreases)
-particle emitted by nucleus, mass & atomic # remains the same (energy content of nucleus only decreases) m =
m =  E/c2
E/c2