M(s)
M(s)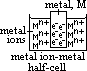
 /V:- pd bet metal and sol containing 1 mol/dm3 of aq metal ions at 25°C (298K) & 1 atm (101325Pa) w/ reference to standard hydrogen electrode
/V:- pd bet metal and sol containing 1 mol/dm3 of aq metal ions at 25°C (298K) & 1 atm (101325Pa) w/ reference to standard hydrogen electrode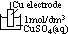
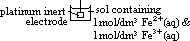
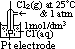
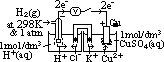
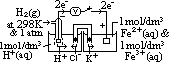
 : pd bet inert Pt electrode & sol w/ 2 aq ions (each of 1 mol/dm3 conc) of same element in diff oxid states at 25°C & 1 atm w/ ref to a standard H electrode
: pd bet inert Pt electrode & sol w/ 2 aq ions (each of 1 mol/dm3 conc) of same element in diff oxid states at 25°C & 1 atm w/ ref to a standard H electrode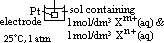

 (reduction) = 0.00V
(reduction) = 0.00V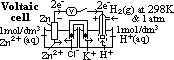
 Zn2+(aq)
Zn2+(aq) H2(g)
H2(g)

 cell: measured by voltmeter
cell: measured by voltmeter cell =
cell =  (reduction) +
(reduction) +  (oxidation)
(oxidation) (Zn2+(aq)/Zn(s)) = -ve
(Zn2+(aq)/Zn(s)) = -ve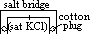
 in form: oxidant + n e-
in form: oxidant + n e-  reductant
reductant => -
=> -  )
) independent of # of moles
independent of # of moles : reduction (or forms +ve plate) wrt H electrode [-ve
: reduction (or forms +ve plate) wrt H electrode [-ve  : oxidation (or forms -ve plate) wrt H electrode]
: oxidation (or forms -ve plate) wrt H electrode]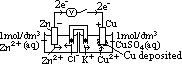

 cell =
cell =  (reduction) +
(reduction) +  (oxidation)
(oxidation) cell: always +ve
cell: always +ve cell = +ve
cell = +ve cell only tells if reaction possible, kinetics decide rate of reaction
cell only tells if reaction possible, kinetics decide rate of reaction cell; large > readily, small > maybe reversible, 0 / -ve > doesn't occur at std conditions (may occur at diff conditions)
cell; large > readily, small > maybe reversible, 0 / -ve > doesn't occur at std conditions (may occur at diff conditions) M(s)
M(s) (reduction) ∝ conc
(reduction) ∝ conc (reduction) more +ve
(reduction) more +ve  more +ve (or less -ve)
more +ve (or less -ve) more -ve/ less +ve)
more -ve/ less +ve)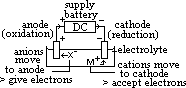
| Voltaic cell | Electrolytic cell |
| chem energy from reaction > elec energy | elec energy used to cause redox reaction |
| reduction at negative cathode | reduction at positive cathode |
| oxidation at positive anode | oxidation at negative anode |
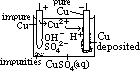
 H+(aq) + OH-(aq)] undergo oxid/reduction [OH- higher in series than SO42- > more likely oxidized; H+ lower in series than Na+ > more likely reduced] [vol H2 twice of vol O2]
H+(aq) + OH-(aq)] undergo oxid/reduction [OH- higher in series than SO42- > more likely oxidized; H+ lower in series than Na+ > more likely reduced] [vol H2 twice of vol O2]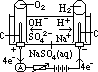
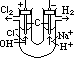
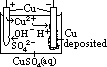
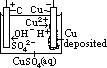
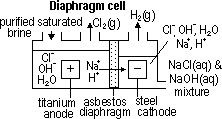
 H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
H+(aq) + OH-(aq)