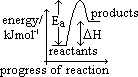
 H: enthalpy change
H: enthalpy change H:- heat change of chemical reaction under const pressure (kJ/mol)
H:- heat change of chemical reaction under const pressure (kJ/mol) H:- enthalpy change measured under standard conditions
H:- enthalpy change measured under standard conditions H +ve
H +ve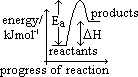 | Ea: activation energy H: enthalpy change H: enthalpy change |
 H -ve
H -ve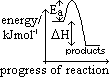 | Ea: activation energy H: enthalpy change H: enthalpy change |
 Hr : heat change when molar quantities of reactants(specified by balance equation) react to for products under standard conditions
Hr : heat change when molar quantities of reactants(specified by balance equation) react to for products under standard conditions Hf : heat change when 1 mole of product formed from elements in the most stable state under standard conditions
Hf : heat change when 1 mole of product formed from elements in the most stable state under standard conditions Hc: heat change (exothermic only) when 1 mole of element / cpd is completely burnt in excess oxygen under standard conditions
Hc: heat change (exothermic only) when 1 mole of element / cpd is completely burnt in excess oxygen under standard conditions H1)> C >(
H1)> C >( H2)> D >(
H2)> D >( H3)> E
H3)> E H4)> E
H4)> E H1 +
H1 +  H2 +
H2 +  H3 =
H3 =  H4
H4 temp = mc
temp = mc T = V
T = V c
c T (
T ( T = initial - final temp)
T = initial - final temp) c
c T/n kJ/mol (of M)
T/n kJ/mol (of M) Hn: heat evolved when 1 mole of H+(aq) from acid reacts with 1 mole of OH-(aq) from base to form 1 mole of water under standard conditions of 1 atmosphere & 25°C
Hn: heat evolved when 1 mole of H+(aq) from acid reacts with 1 mole of OH-(aq) from base to form 1 mole of water under standard conditions of 1 atmosphere & 25°C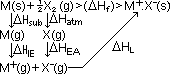
 Hsub, enthalpy change of sublimation of element: heat absorbed to convert solid element into 1 mole of gaseous atom
Hsub, enthalpy change of sublimation of element: heat absorbed to convert solid element into 1 mole of gaseous atom Hsub)> M(g)
Hsub)> M(g) Hsub)> M(g) = M(s) >(
Hsub)> M(g) = M(s) >( Hfusion)> M(l) >(
Hfusion)> M(l) >( Hvap)> M(g)
Hvap)> M(g) Hsub =
Hsub =  Hfusion +
Hfusion +  Hvap = enthalphy change of (fusion of solid M+ vaporization liquid M)
Hvap = enthalphy change of (fusion of solid M+ vaporization liquid M) Hsub can be also called enthalpy change of atomization,
Hsub can be also called enthalpy change of atomization, Hatomisation: energy absorbed to change a subs from solid, liquid or gaseous state into 1 mole of gaseous atoms; M(s/l/g) > M(g)
Hatomisation: energy absorbed to change a subs from solid, liquid or gaseous state into 1 mole of gaseous atoms; M(s/l/g) > M(g) Hatomisation = ½ bond energy]
Hatomisation = ½ bond energy] HIE, 1st ionisation energy: min energy absorbed to remove 1 mole of most loosely bound valence electrons in ground state from 1 mole of isolated, gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of isolated gaseous singly-charged positive ions
HIE, 1st ionisation energy: min energy absorbed to remove 1 mole of most loosely bound valence electrons in ground state from 1 mole of isolated, gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of isolated gaseous singly-charged positive ions HIE)> M+(g)
HIE)> M+(g) HEA: energy evolved when 1 mole of valence electrons is added to 1 mole of isolated gaseous atoms to from 1 mole of isolated, gaseous singly-charge negative ions
HEA: energy evolved when 1 mole of valence electrons is added to 1 mole of isolated gaseous atoms to from 1 mole of isolated, gaseous singly-charge negative ions HL: energy evolved when isolated, gaseous anions & cations combine to form 1 mole of ionic solid
HL: energy evolved when isolated, gaseous anions & cations combine to form 1 mole of ionic solid HL)> M+X-(s)
HL)> M+X-(s)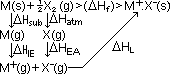
 Hsolution: energy change when 1 mole of ionic solid dissolved in such an amt of water that further dilution causes no more heat change (solution of infinite dilution)
Hsolution: energy change when 1 mole of ionic solid dissolved in such an amt of water that further dilution causes no more heat change (solution of infinite dilution) Hsolution)> M+(aq) + X-(aq)
Hsolution)> M+(aq) + X-(aq) Hhyd: energy evolve when 1 mole of gaseous ions is hydrated in water to form aqueous ions
Hhyd: energy evolve when 1 mole of gaseous ions is hydrated in water to form aqueous ions Hhyd)> M+(aq)
Hhyd)> M+(aq)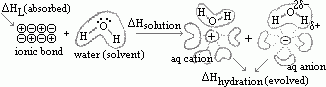
 HBE (bond enthalpy / bond dissociation energy)
HBE (bond enthalpy / bond dissociation energy) HBE)> X(g) + Y(g)
HBE)> X(g) + Y(g) H1)> XYn-1(g) + Y(g)
H1)> XYn-1(g) + Y(g) H2)> XYn-2(g) + Y(g)
H2)> XYn-2(g) + Y(g) Hn)> X(g) + Y(g)
Hn)> X(g) + Y(g) H1 +
H1 +  H2 + ... +
H2 + ... +  Hn)/n
Hn)/n HBE increases w/:
HBE increases w/: HBE)
HBE)