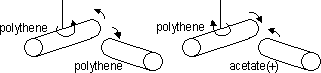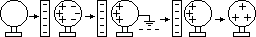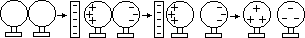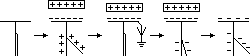ELECTROSTATICS
charges: +/- (due to electrons which are -ve in charge, 1 e-: 1.6 × 10-19C)
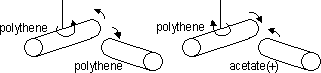
-when polythene rubbed w/ wool: e-s rubbed off wool & onto polythene > -ve charge on polythene
like charges: attract, unlike charges: repel
Electrostatic charging by: -friction & -induction
Charging by induction
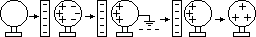
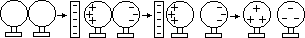
Gold-leaf electroscope: to detect charges
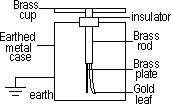
Charging GL electroscope by induction
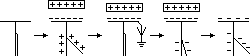
when charged rod brought near to charged electroscope
-if same charge > leaf divergence increases (to identify charge)
-if opposite charge / neutral > leaf divergence decreases
Conductors; metals + C- have free e-s that move and conduct electricity
Insulators; non-metals (plastic, wood, glass, rubber,..)- e-s firmly bounded to nucleus
Uses of electrostatics
-dust extraction
-spray painting
-photocopiers
-van de-Graph generators; produce v.high voltages > accelerate sub-atomic particles
Hazards of electrostatics
build-up of charges by friction can cause sparks > fires (pd v.high > air conducting > charge move bet 2 plates instantaneously > form spark)
-lightning: lightning conductors needed to reduce/ eliminate charge build-up
-airplanes (charging due to air resistance): tires conduct charges > charges leak to ground,
-trucks: chain dragging on ground > disperse charges
Back to 'A' level notes index
Back to notes index