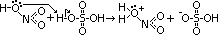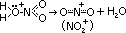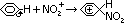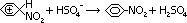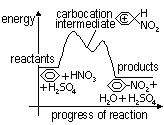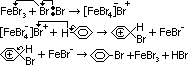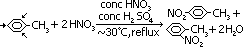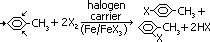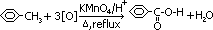AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
aromatic h/c= h/c w/ benzene ring
Alkylbenzenes
general formula: C6+nH6+2n (n = 0,1,..)
Benzene
molecular formula: C6H6
structural formula: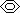
-consists of 6 sp2-hybridised C atoms, 6 π electrons delocalised forming 2 electron cloud rings above + below benzene ring, all C-C bonds same (longer than C-C double bond, but shorter than C-C single bond)
benzene has resonance stabilised structure
Physical properties
-colourless liquid w/ characteristic smell
-benzene less dense than water & immiscible w/ water
-carcinogenous (toxic vapour, excessive inhalation of vapour can led to anaemic leukaemia)
(benzene burns w/ yellow sooty flame)
Nitration of benzene
reagents: nitration mixture (conc HNO3 + conc H2SO4)
conditions: temperature: < 55°C, heat under reflux
equation: C6H6 + HNO3 >(conc HNO3 + conc H2SO4, under reflux < 55°C)> C6H5-NO2 + H2O
[benzene + nitric acid > nitrobenzene + water]
observatyion: lower yellow oily liquid (nitrobenzene) formed
Mechanism of electrophilic subtstitution (nitration of benzene)
- electrophilic nitronium/nitryl ion, NO2+, formed
--protonating nitric acid
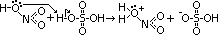
HNO3 (conc) + H2SO4 (conc) > HSO4- + H2O + NO2+
--removal of water molecule from protonated nitric acid > electrophilic nitronium ion
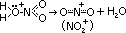
-Electrophilic nitronium ion attacks benzene ring > positive carbocation intermediate
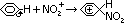
-H+ removed from carbocation intermediate by nucleophilic HSO4- > nitrobenzene
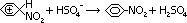
delocalisation of 6 π electrons preserves benzene ring structure > substitution, not addition, occurs in nitration
temperature of reaction: 50-55°C, higher temp: formation of dinitro-, trinitro- benzene
Energy diagram of nitration of benzene
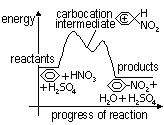
Halogenation
reagent: X [Br(l)/Cl(g)]
condition: catalyst: 'halogen carrier'- finely divided iron or iron(III) bromide, FeBr3, room temp
equation: C6H6 + X2 >(Fe)> C6H5-X + HX [benzene + halogen molecule > halogenoarene + hydrogen halide]
observation: excess benzene > red Br / yellow -green Cl decolourised (colourless products)
bromination of benzene w/ Fe: electrophilic subs mechanism like nitration (electrophilic Br+/Cl+ produced)
2Fe + 3Br2 > 2FeBr3
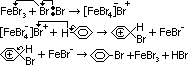
Methylbenzene
molecular formula: C6H5CH3
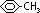
C6H5 part is planar
C-CH3 part is tetrahedral
Physical properties
-colourless liquid w/ characteristic smell
-insoluble in water > upper immiscible layer
-good organic solvent (replace toxic benzene)
Reactions of methylbenzene:
Electrophilic subs of H in benzene ring
-nitration
-halogenation
--bromination
--chlorination
Side-chain methyl group
-FR substitution of H atoms of methyl group
-oxidation of methyl group
Electrophilic substitution
methyl group, -CH3: more reactive than benzene
Nitration
reagent: nitrating mixture of conc HNO3 + conc H2SO4
conditions: under reflux, ~ 30°C
equation:
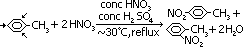
nitrating of methylbenzene produces 2 isomers: 1-methyl-2-nitrobenzene & 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene (ratio 2:1)
Position of substitution in benzene ring
Group G in benzene ring determines position of substitution
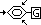
substitution occurs at carbon 2,4,6 if G is
-alkyl group
-hydroxy group
-amino group
-halogeno group
(groups don't have double / triple bonds)
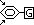
substitution occurs at carbon 3/5 if G is
-cyano group
-nitro group
-carboxylic group
-carbonyl group
(groups have double / triple C bonds)
Halogenation
substitution of H atom of benzene ring by halogen occurs through electrophilic subs mechanism
reagent: X [Br(l)/Cl(g)]
condition: catalyst: 'halogen carrier'- finely divided iron or iron(III) halide, [FeBr3/FeCl3], room temp
equation:
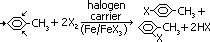
[1-X-2-methylbenzene/1-X-4-methylbenzene formed in ration= 2:1]
observation: excess methylbenzene > red Br / yellow -green Cl decolourised (colourless products)
Reactions involving side-chain methyl group of methylbenzene
Halogenation: Free radical substitution
reagent: halogen, Cl2 (g) / Br2(l)
condition: boiling methylbenzene (in absence of halogen carrier) + UV light
equation: C6H5-CH3 + X2 >(reflux at bp of methylbenzene)> C6H5-CH2X+ HX
[methylbenzene + halogen > halogenomethylbenzene + hydrogen halide]
excess halogen > multi substituted product
Oxidation
methylbenzene oxidised to carboxylic acid
reagent: acidified potassium manganate (VII), KMnO4(aq)/H2SO4(aq) (not HCl/HNO3 as they react w/ KMnO4)
condition: heat under reflux
equation:
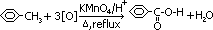
[methylbenzene >(oxidation)> benzoic acid + water]
observation: if excess methyl benzene:
-purple KMnO4 decolourised
-on cooling > white needle-shaped crystals of benzoic acid (benzoic acid + PbCl2: soluble in hot water)
(only C atom attached to benzene ring will form acid, other C atoms oxidised to CO2 + water)
Back to 'A' level notes index
Back to notes index