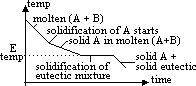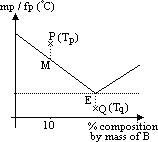PHASE DIAGRAMS
phase: homogenous part of a system that is distinct by phase boundary from other parts of the system
phase diagram: graphical plots of experimentally determined results (saturated vapour pressure plotted against temp)
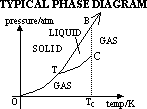
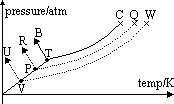
PHASE DIAGRAM FOR SINGLE COMPONENT SYSTEM
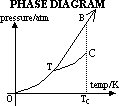
phase diagrams have:
(1)regions where solid/liquid/gas exist depending on condition
(2)lines which represent pressure & temp where different phases of the matter can exists (depending on conditions)
Line OT: conditions for existence of solid & gas phase in eqlbm
Line TB: conditions for existence of solid & liquid phase in eqlbm
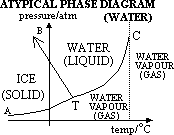
[typical case: solid denser than liquid,
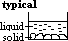
atypical case (water & ice): solid less dense than liquid]
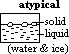
Line TC: conditions for existence of liquid & gas phase in eqlbm
(3)points
T = triple point: temp & pressure when all 3 phases coexist in eqlbm
C = critical pt: temp & pressure beyond which liquid & gas are indistinguishable-have same densities & no phase boundary
[below critical temp
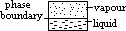
above critical temp: no liquid phase exists
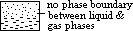
vapour pressure exerted at critical pt = critical pressure = min pressure that must be applied to gas or vapour at critical temp to liquefy it
beyond critical temp gas / vapour can't be liquefied despite large pressure]
Phase diagrams of
(1)normal subs (CO2); TB +ve gradient (ie mp increases w/ increased pressure)
(2)atypical subs (water); TB -ve gradient (ie mp decrease w/ increased pressure) [due to expansion when ice forms or contraction when water formed]
(3)helium; TB // to y-axis (pressure) as density of liquid & solid are equal above triple pt pressure
-liquid hydrogen obtained by adding solute to helium (hydrogen ,argon, nitrogen) as it lowers vapour pressure > lowers mp

Effect of non-volatile solute on vapour pressure of water (ie liquid)
-solute added: vapour pressure decrease (more conc > decreased more) (solute for water- glucose, NaCl, antifreeze)
-due to intermolecular F of attraction bet solvent molecules (water) & solute molecules (glucose) or solute particle (ions) > solvent molecules less likely to escape from surface to form vapour > vapour pressure decreases > mp decrease, bp increase
[for gas, eg He, other gases, eg Ar, N2, H2 can be used to lower vapour pressure]
eg antifreeze (ethane-1,2-diol) in car radiators- prevent freezing, salt & sand sprinkled on ice/snow- melt ice/snow
PHASE DIAGRAM FOR TWO-COMPONENT SYSTEM
melting pt, (mp): temp at which solid changes to liquid under 1 atm
freezing pt, (fp): temp at which liquid changes to solid under 1 atm
pure subs: -melts & freezes at sharp const temp, ie mp = fp
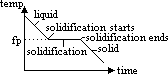
mixture(impure sub):
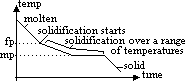
-mp: temp at which solid just start to melt under 1 atm
-fp: temp at which liquid just start to solidify under 1 atm
-mp & fp different; melts & freezes over range of temp > mp lower than fp
Eutectic mixture, EM: mixture of >1 subs w/ lowest mp / fp (which are equal) out of all the possible compositions of he mixture [melts / freezes at fixed temp = eutectic temp w/o any change in mass composition = eutectic composition]
EM not cpd; -(1)existence of separate crystals of components (not other cpd crystals), -(2)composition & mp of eutectic mixture change w/ change in pressure
Phase diagram of 2 component system (Sn/Pb, camphor/naphthalene, NaCl/water)
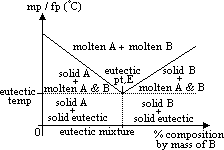
has 2 intercepting lines which meet at eutectic pt, E
left hand side of eutectic pt: B acts as impurity of A (lowers mp of A)
right hand side of eutectic pt: A acts as impurity of B
x-axis: % composition of molten mixture at diff temp
cooling curve of 2 component system from molten to solid state on left side of E pt:
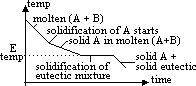
cooling a mixture containing 10% B from Tp to Tq
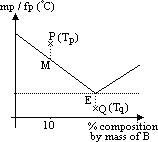
from TM to TE: % composition of B of molten mixture follows line ME, ie increases (due to formation of more solid A)
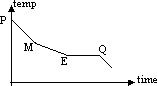
P to M: 
M to E: 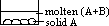
Q onwards: 
Uses of tin/lead alloys
electrician solder: 67% Sn, 33% Pb, due to lowest mp and solidifies fast
plumber's solder: 33% Sn, 67% Pb, due to long freezing range (high % of Pb => soft alloy > can bend easily)
(mp of Sn/Pb alloy can be lowered by adding 3rd component)
alloy: mixture of main metal w/ certain proportions of other metals / non-metals
used to improve / change properties of pure element
strengthen: atom of added element prevents sliding of metal layers
increase corrosion resistance: stainless steel- alloy of Fe, Ni, Cr: forms surface film of impervious metal oxides which resist rust & tarnish
lower mp: Sn/Pb alloys as solder
Uses of NaCl(aq)
-fp of water lowered (causes ice to melt if NaCl is sprinkled)
-mixture of NaCl & ice = freezing-mixture, more conc NaCl lower fp
unusual phase diagram of 2 component system
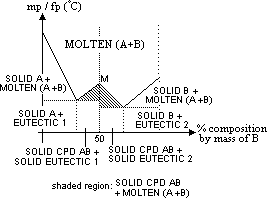
cpd formed derived from % composition as max pt M
Back to 'A' level notes index
Back to notes index