| fossil fuel | sulphur content (% by mass) |
| coal | bet 0.5% & 6% |
| gasoline | 0.04% |
| diesel | 0.22% |
| fuel oil bet | 0.75% & 3% |
 2SO3(g) [95% conversion under these conditions]
2SO3(g) [95% conversion under these conditions]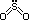
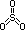
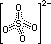
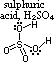
| sulphite, SO32- | sulphate, SO42- | |
|---|---|---|
| + dil HNO3 | choking gas smell of burning sulphur; turns Cr2O7-/H+ green > gas is SO2 SO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) > SO2(g) + H2O(l) | no reaction |
| + Ba(NO3)2(aq), + dil HNO3 | white ppt, soluble in acid SO32-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) > BaSO3(s) (white ppt) | white ppt, insoluble in acid SO42-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) > BaSO4(s) (white ppt) |