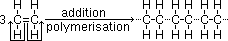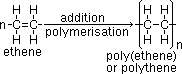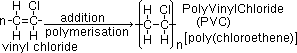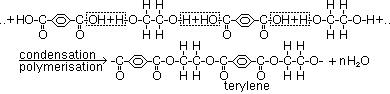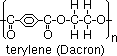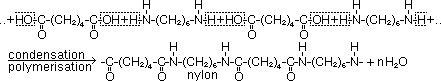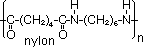POLYMERISATION
polymerisation: -addition polymerisation, -condensation polymerisation
Addition polymerisation
addition polymerisation = reaction where unsaturated monomers [(substituted) alkenes] joined together to form large addition polymer (formed by free radical addition of monomers when pi-electrons from double bond form new covalent C-C bonds)
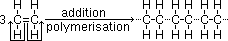
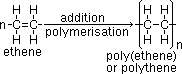
poly(ethene): in packaging & for plastics (bags + toys)
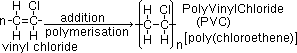
PVC: electrical insulation, drainage pipes, rain coats
-poly(propene): for ropes & packaging
-poly(tetrafluoroethene), PTFE (Teflon): v. smooth, for burrete stop cocks, non-stick frying pans
-poly(phenylethene) (polystyrene): for insulation & packaging
-poly(methyl-2-methylpropenoate) (perspex): aka artificial glass, v.transparent, for glass substitute
-poly(propenonitrile), (polyacrylonitrile/ Acrilan/ Orlon): for acrylic fibres for clothing, blankets & carpets
monomer >(polymerisation)> -[repeating unit]n-
Properties of addition polymers(polyalkenes):
-same empirical formula & % composition as monomer (no atoms added/lost)
-not hydrolysed by alkalis
-non-biodegradable > difficult to dispose, put in land fill > pollution (polymer w/ C & H only: burnt > CO2 + H2O, polymers like PVC & acrylic fibre: if burnt > harmful products emitted, eg HCl & HCN gas)
Condensation polymerisation
-reaction where 2 bifunctional monomers join w/ removal of simple molecule(usually water)(condensation / addition-elimination reaction) to form large molecule
2 types of condensation polymers: polyester & polyamide
-Formation of polyester
monomers: benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid, ethane-1,2-diol
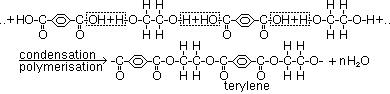
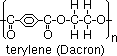
terylene: clothing material [mixed w/ wool /cotton > drip-dry clothes (don't absorb water)]
-Formation of polyamides
polyamides: from dicarboxylic acid & diamine or from an amino acid(amino acid reacts w/ itself due to both carboxyl and amine group of 2 diff molecules reacting)
-Formation of nylon
monomers: hexane-1,6-dioic acid & hexane-1,6-diamine
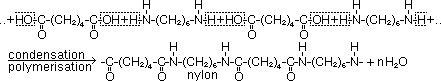
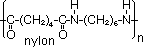
nylon: for stockings (due to fineness, strength, elasticity & cheapness), fishing lines, clothing, tooth-brush bristles
Properties of condensation polymers:
-diff empircal formula & % compostion from monomers (molecule removed)
-weakened by acid & alkali (hydrolyses amide/ester bond)
Back to 'A' level notes index
Back to notes index