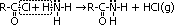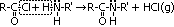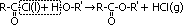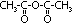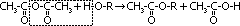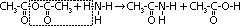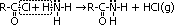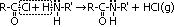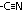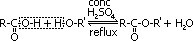
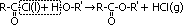
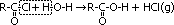
| Acid chloride, CH3C(=O)Cl | Halogenoalkane, CH3CH2Cl | Halogenobenzene, C6H5Cl |
| most reactive CH3C(=O)Cl + H2O >(room temp)> CH3C(=O)OH + HCl | no reaction w/ water but w/ dil NaOH when boiling under reflux CH3CH2Cl + NaOH >(heat, reflux)> CH3CH2OH + NaCl | least reactive: no reaction w/ water, but only w/ conc NaOH heated under pressure C6H5Cl + conc NaOH >(heat under pressure)> C6H5O-Na+ + NaCl + H2O |
| electronegative Cl atom & O atom pull e-s away from carbonyl C atom > C atom more +ve > more susceptible to nucleophilc substitution | polar C-Cl bond > C atom a bit +ve > susceptible to nucleophilic substitution | delocalistaion of Cl e- into benzene ring > C-Cl bond not very polar anymore > not very susceptible to nucleophilic substitution |