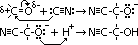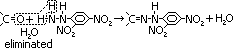CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
carbonyl cpds: ketones + aldehydes
MF: CnH2nO
functional group: aldehyde: R-C=(O)H, ketone: R-C(=O)-R
Physical properties
-methanal: only carbonyl cpd gas at rtp
-aldehydes: strong, pungent smell
-ketones: pleasant smell
-polar bonds > permanent dipole-dipole attraction > higher mp, bp than expected
-lower members of carbonyl cpds: soluble in H2O, higher members (stronger attraction) > only in organic solvents
Formation of carbonyl cpds
aldehydes:
oxidation of 1° alcohols
condition: heat + distil
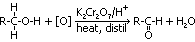
ketones:
oxidation of 2° alcohols
condition: heat under reflux
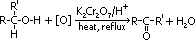
Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl group
O atom draws e-s from C atom > polar bond, C atom δ+
-ve nucleophile attaches to C atom
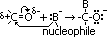
reagent: conc sol of aq KCN [KCN > K+ + CN-, H2O  OH- + H+ => H+ + CN-
OH- + H+ => H+ + CN-  HCN]
HCN]
condition: room temp

Mechanism of nuclephilic addition
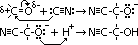
Condensation reaction
reagent: 2,4-denitrophenylhydrazine (dissolved in aq alcoholic solvent > orange yellow sol)
condition: room temp
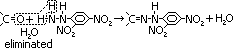
observation: immediate orange-yellow precipitate formed
Reduction to alcohol
reagent: LiAlH4
condition: ice-cold temp (0°C -10°C)
R-C(=O)H + 2[H] >(LiAlH4/dry ether, < 10°C)> R-CH2OH
Triodomethane test
reagent: alkaline aq I sol
condition: warm reaction mixture
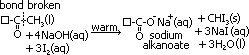
observation: yellow ppt of CHI3
Reactions to test for aldehydes
Tollen's Reagent
reagent: diammine silver ion in alkaline sol (Tollen's reagent) (colourless)
[preparation of Tollen's reagent:
NaOH(aq) + AgNO3(aq) > AgOH(s)(brown ppt)
AgOH(s) + 2NH3(aq)(excess) > Ag(NH3)2+(aq) + OH-(aq)]
condition: warm mixture over water bath
observation: shiny reflecting metallic silver
R-C(=O)H + 2Ag(NH3)2+ + 3OH- > 2Ag + RC(=O)O- + NH3 + H2O (redox reaction)
Fehling's solution
reagent: Fehling's solution (deep blue sol- contains Cu2+(aq) in alkaline sol)
[Fehling's solution: from Fehling's sol A (CuSO4(aq)-blue sol) + Fehling's sol B (aq Na K tartrate + aq NaOH-colourless)]
condition: warm over water bath
observation: red ppt of Cu2O formed (copper(I) oxide-red, copper(II) oxide-black)
R-C(=O)H + 2Cu2+ + 5OH- > Cu2O + R-C(=O)O- + 3H2O (redox reaction)
Oxidation
reagent: acidified oxidising agent: K2Cr2O7/H+ or KMnO4/H+
condition: heat under reflux
observation: excess aldehyde- K2Cr2O7: orange > green (KMnO4: purple > colourless)
R-C(=O)H + [O] >(KMnO4, heat, reflux)> R-C(=O)OH
(ketones: resistant to oxidation > no reaction w/ Tollen's reagent, Fehling's sol or oxidising agent)
Back to 'A' level notes index
Back to notes index
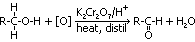
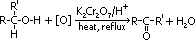
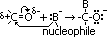
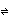 OH- + H+ => H+ + CN-
OH- + H+ => H+ + CN- 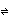 HCN]
HCN]