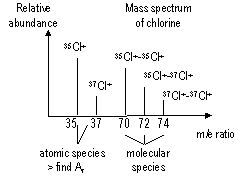ATOMS, MOLECULES & STOICHIOMETRY
Atoms, molecules & ions
Atom: smallest indivisible part of element, has neutrons, protons + electrons, can't be changed by chemical reactions (only nuclear reactions 14N >(cosmic radiation) >14C)
Molecule: smallest part of element / compound that exists by itself
Ion: charged particle (+/-)
Relative atomic mass RAM: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon scale
hydrogen scale: H atom = lightest atom > given relative mass (RM) of 1 unit (mass of 1 atom of (element/H) x 1.0000)
oxygen-16 scale: O atom given RM of 16 units (mass of 1 atom of (element/16O) x 16.0000)
carbon-12 scale: C atom > given RM of 12 units (mass of 1 atom of (element/12C) x 12.0000)
RAM = mass of 1 atom of element on a scale w/ mass of 1 atom of 12C=12.000 units exactly
RAM of naturally occurring elements
naturally occurring elements: 2/> isotopes > RAM = weighted av. of RM of isotopes, RAM of an isotope = relative isotopic mass (RIM), RAM of naturally occurring element = (RIM x abundance of)(isotope 1 + isotope 2 + 3+...)
RIM of an isotope = mass of 1 atoms of isotope on a scale where 1 atom of 12C is 12.0000
RAM & Molar mass
RAM: no units, Molar mass: numerical value of RAM expressed in g/mol (molar mass = mass of 1 mole (6.02 x 1023 particles) of element
Relative molecular mass (RMM)(Mr): mass of 1 molecule of element / compound on 12C scale
Relative formula mass (RFM): mass of ion(ic compound) on 12C scale
Use of mass spectrometer to calculate RAM
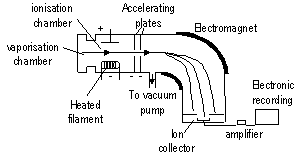
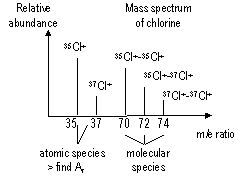
high vacuum / low pressure inside > prevent complications from air molecules
in vaporisation chamber: subs > gaseous/vapour state, subs passed through ionisation chamber where heated filament emits fast moving e-'s > knock off valence e-'s in molecules/atoms > +ve ions (mostly +1, +2 possible) > beam of +ve ions > go through mag. field > deflected ( e/m; greater deflection: greater charge, lesser mass) > > detected by ion collector > amplified > recorded as mass spectrum
(ions of diff e/m ratio focused into ion collector 1 by 1 > recorded)
molecules in mass spectrometer > covalent bonds broken > fragments, largest m/e ratio = RMM
if element / molecule charge = +2 > m/e ratio: e = 2 (m = mass) > plotted in mass spectrum
a mole = quantity of particles(molecules/atoms,which is equivalent to # of atoms in 12.0000g of 12C (ie 6.02 x 1023 particles), 6.02 x 1023 = Avagadro's constant, L
1 mole used as: -mass of 1 mole of elements is known(given by periodic table) the chemical equation gives ratios of # of particles reacted & formed
# of moles x Mr = mass in 'g', # of moles x 22.4dm3/mol (stp) =vol in dm3 (gas) (stp: 1atm, 0°C)
at const temp + pressure vol ratio of gases = mole ratios
Gay-Lussac's law: at the same temp & pressure, gases react in vol.'s which bear simple ratios to one another & also to the products if gaseous
Formulae of compounds: -empirical, -molecular, -structural
Empirical formula: shows simplest ratio of atoms in molecule of compound
Molecular formula: shows actual ratio of atoms in molecule
Structural formula: shows arrangement of atoms in molecule
Combustion of a hydrocarbon: CxHy (g) + (x+y/4)O2 (g) > xCO2 (g) + y/2H2O (g-100°C/l)
EF found from data of products
Concentration: g/dm3 or mol/dm3 [mol/dm3 = molar conc; # of moles in 1 dm3]
Back to 'A' level notes index
Back to notes index